Tax Planning

Tax Planning: A Comprehensive Overview
Tax planning is a crucial part of personal and business financial management. It involves analyzing your financial situation and making strategic decisions to legally minimize your tax liability while aligning with your broader financial goals.
🧠 What is Tax Planning?
Tax planning is the process of organizing your finances in such a way that you can take full advantage of the various deductions, exemptions, allowances, and rebates permitted by law to reduce your tax burden.
🎯 Objectives of Tax Planning
✅ Minimize Tax Liability – Reduce the amount of tax payable through legal means.
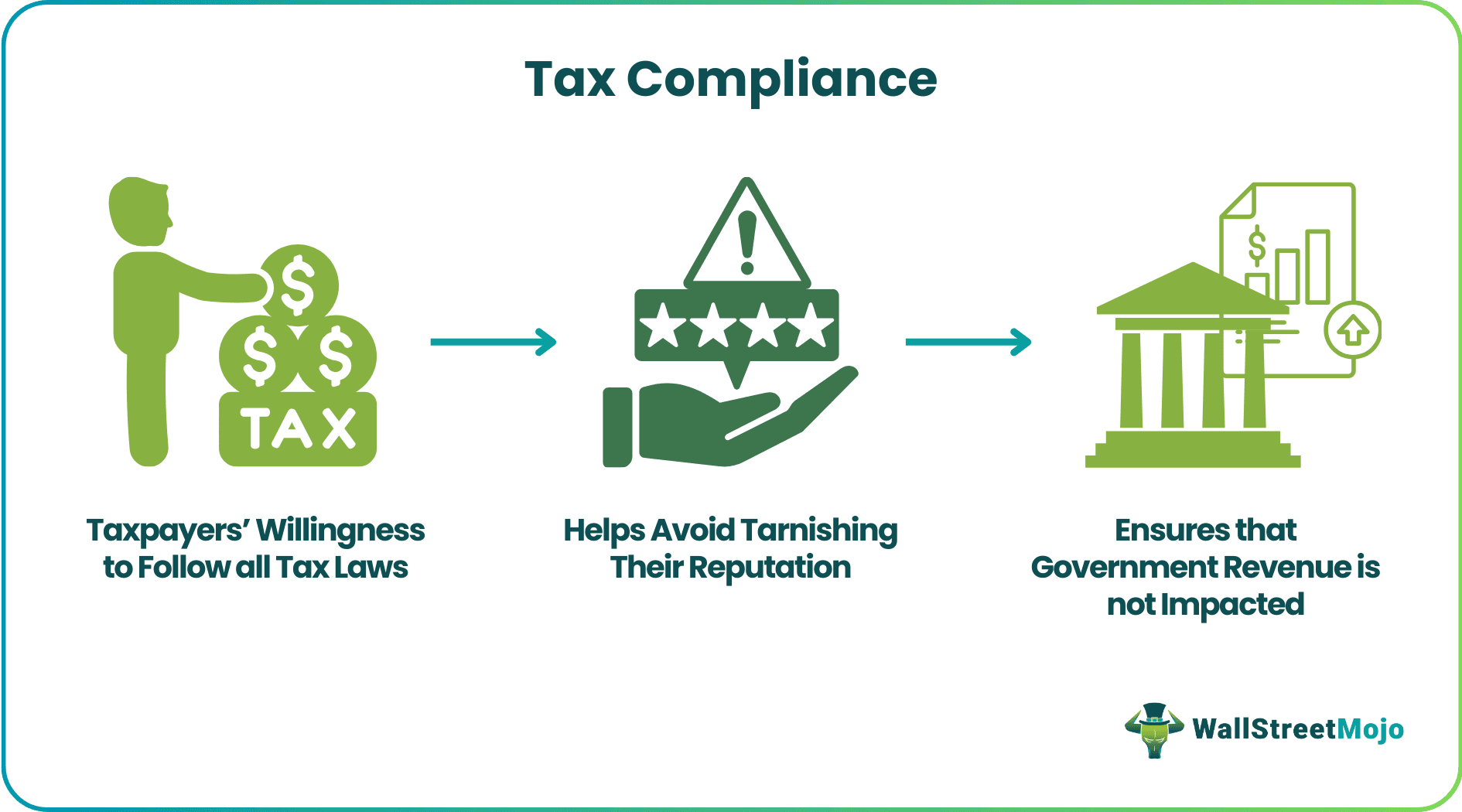
💼 Ensure Compliance – Meet all legal requirements and avoid penalties or scrutiny.
📈 Optimize Investments – Choose tax-saving instruments that also help grow wealth.
🛡️ Increase Savings – Retain more of your earnings for future use.
🧾 Efficient Resource Utilization – Allocate resources wisely with tax impact in mind.
📚 Types of Tax Planning
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Short-term Tax Planning | Planning for a financial year to minimize tax liability without long-term commitments. |
| Long-term Tax Planning | Planning well in advance with long-term tax-saving investments like PPF, ELSS, etc. |
| Permissive Tax Planning | Using methods allowed by law (e.g., Section 80C deductions). |
| Purposive Tax Planning | Planning with specific financial objectives in mind (e.g., retirement, education). |
🧾 Key Tax Planning Strategies (India-specific, but concepts apply broadly)
👨👩👧👦 For Individuals
Utilize Section 80C (Up to ₹1.5 lakh)
PPF (Public Provident Fund)
ELSS (Equity-Linked Savings Scheme)
Tax-saving FDs (5-year)
LIC premiums
Home loan principal repayment
Additional Deductions
Section 80D – Health insurance premiums
Section 24(b) – Home loan interest (up to ₹2 lakh)
Section 80G – Donations to charities
Section 80E – Education loan interest
Invest in Tax-free Instruments
PPF
Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana
Municipal bonds (in some countries)
Choose the Right Tax Regime
Old regime (with deductions) vs. New regime (lower tax rates, no deductions)
🏢 For Businesses
Depreciation on assets
Business expenses (travel, rent, salaries, etc.)
Carry forward losses
Investment in R&D and other tax-incentivized sectors
HUF (Hindu Undivided Family) structuring (India-specific)
💡 Tips for Effective Tax Planning
Start early in the financial year (avoid March rush)
Maintain records of all investments and expenses
Use digital tools or consult a tax advisor
Review tax law updates every year
Combine tax planning with financial planning for goals like retirement, education, etc.
🧮 Example: Tax Planning Scenario (India)
Suppose your annual income is ₹10,00,000. Here’s a possible tax-saving plan:
| Investment / Expense | Deduction Claimed |
|---|---|
| PPF contribution | ₹50,000 |
| ELSS investment | ₹50,000 |
| Life insurance premium | ₹25,000 |
| Health insurance premium (80D) | ₹25,000 |
| Home loan interest (Section 24b) | ₹2,00,000 |
| Total Deduction | ₹3,50,000 |
This reduces your taxable income significantly, lowering your tax outgo.
🧠 Conclusion
Tax planning is not about evading taxes—it’s about being smart, proactive, and compliant. By understanding the tax laws and using the available provisions wisely, you can legally reduce your tax burden, improve your cash flow, and achieve your financial goals faster.
Don't Suffer in Silence, Let Us Help You Get The Justice You Deserve!
Contact us now for a free consultation